Made by Mike_Zhang
数据结构与算法主题:
Definition for a binary tree node:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class TreeNode {int val;int val) { this .val = val; }int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {this .val = val;this .left = left;this .right = right;
1 Binary Tree Traversal 1.1 Pre-order Traversal
First visit the root , then traverse the left subtree, finally traverse the right subtree.
Binary Tree Preorder Traversal LeetCode Problem #144
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();return outList;void PreOrder (TreeNode inRoot, List inList) {if (inRoot == null ) {return ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();new Stack <>();TreeNode curr = root;while (curr != null || !stack.empty()) {if (curr != null ) {else {TreeNode node = stack.pop();return outList;
1.2 In-order Traversal
First traverse the left subtree, then visit the root , finally traverse the right subtree.
Binary Tree Inorder Traversal LeetCode Problem #94
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();return outList;void InOrder (TreeNode inRoot, List inList) {if (inRoot == null ) {return ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();new Stack <>();TreeNode curr = root;while (curr != null || !stack.empty()) {if (curr!=null ) {else {TreeNode node = stack.pop();return outList;
1.3 Post-order Traversal
First traverse the left subtree, then traverse the right subtree, finally visit the root .
Binary Tree Postorder Traversal LeetCode Problem #145
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();return outList;void PostOrder (TreeNode inRoot, List inList) {if (inRoot == null ) {return ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();new Stack <>();TreeNode curr = root;TreeNode last = null ;while (curr != null || !stack.empty()) {if (curr != null ) {else {TreeNode node = stack.peek();if (node.right != null && last != node.right) {else {return outList;
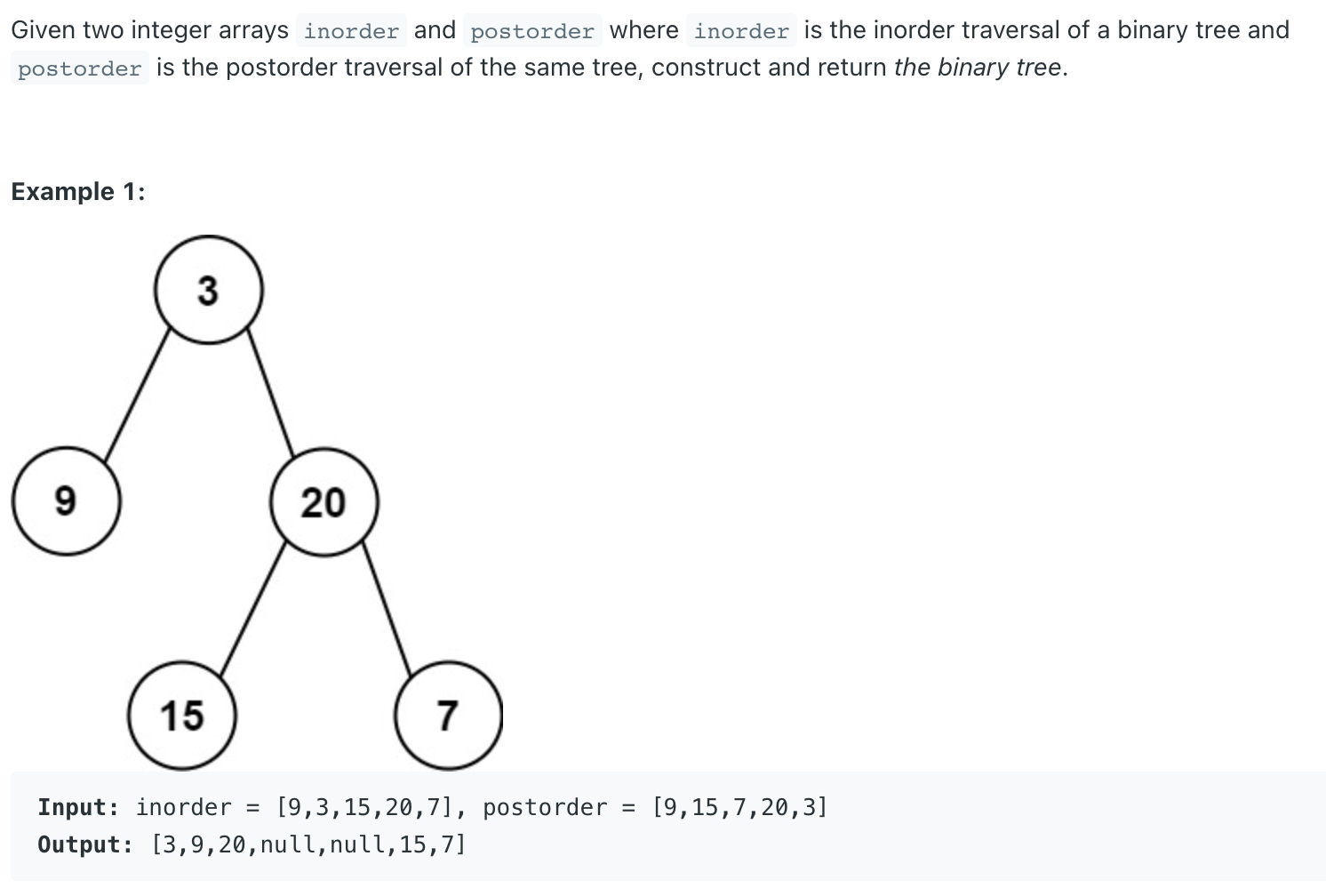
1.4 Construct Binary Tree from two kinds of Traversal Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal LeetCode Problem #106
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {public TreeNode buildTree (int [] inorder, int [] postorder) {if (inorder.length == 0 ) {return null ;int rootVal = postorder[postorder.length-1 ];int i=0 ;for (i=0 ;i<inorder.length;i++) {if (inorder[i]==rootVal) {break ;int [] inLeft = Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,0 ,i);int [] inRight = Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,i+1 ,inorder.length);int [] postLeft = Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder,0 ,i);int [] postRight = Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder,i,inorder.length-1 );TreeNode outTree = new TreeNode (rootVal);return outTree;
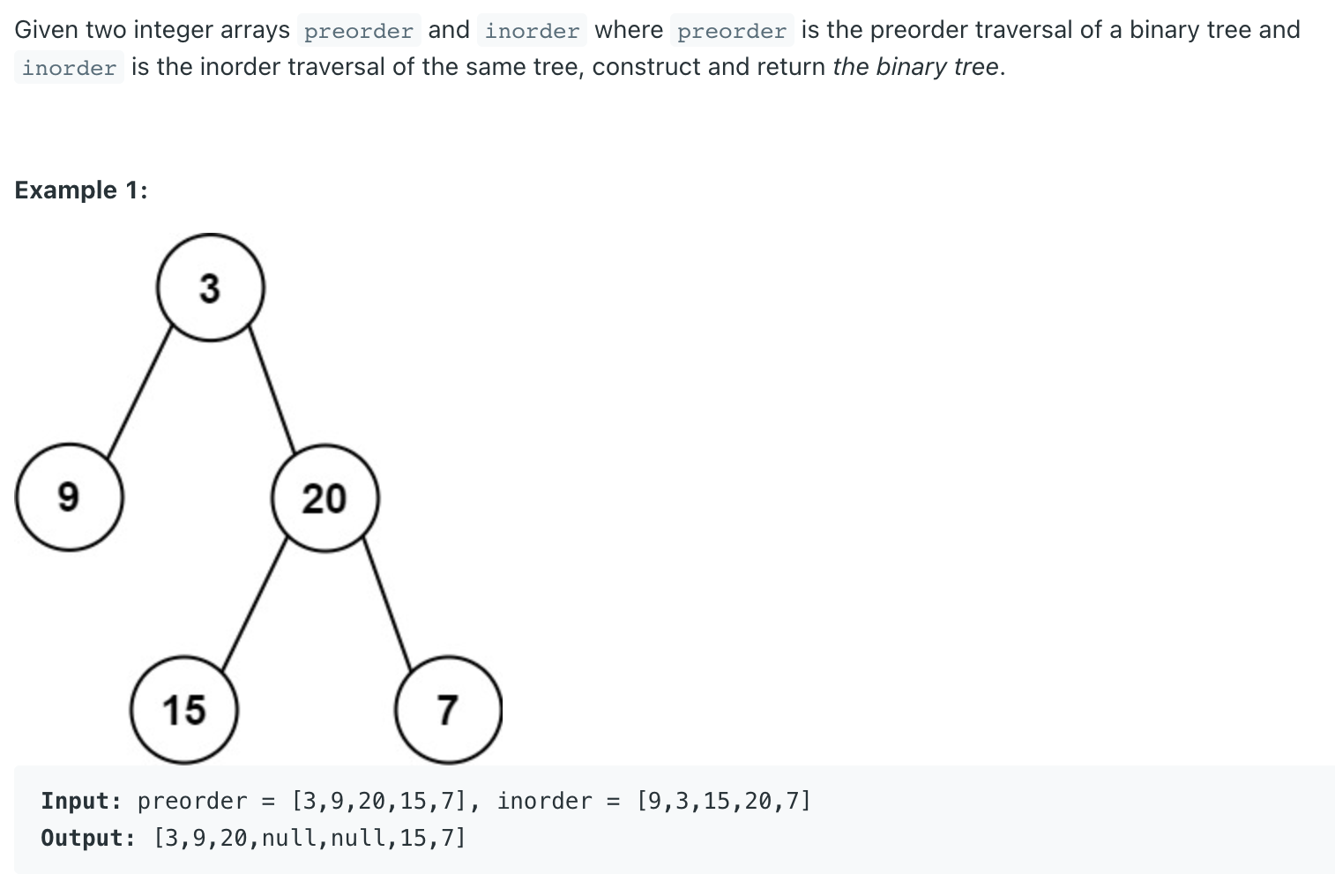
Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal LeetCode Problem #105
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {public TreeNode buildTree (int [] preorder, int [] inorder) {if (inorder.length == 0 ) {return null ;int rootVal = preorder[0 ];int i = 0 ;for (i=0 ;i<inorder.length;i++) {if (inorder[i] == rootVal) {break ;int [] inLeft = Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,0 ,i);int [] inRight = Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,i+1 ,inorder.length);int [] preLeft = Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder,1 ,i+1 );int [] preRight = Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder,i+1 ,inorder.length);TreeNode outTree = new TreeNode (rootVal);return outTree;
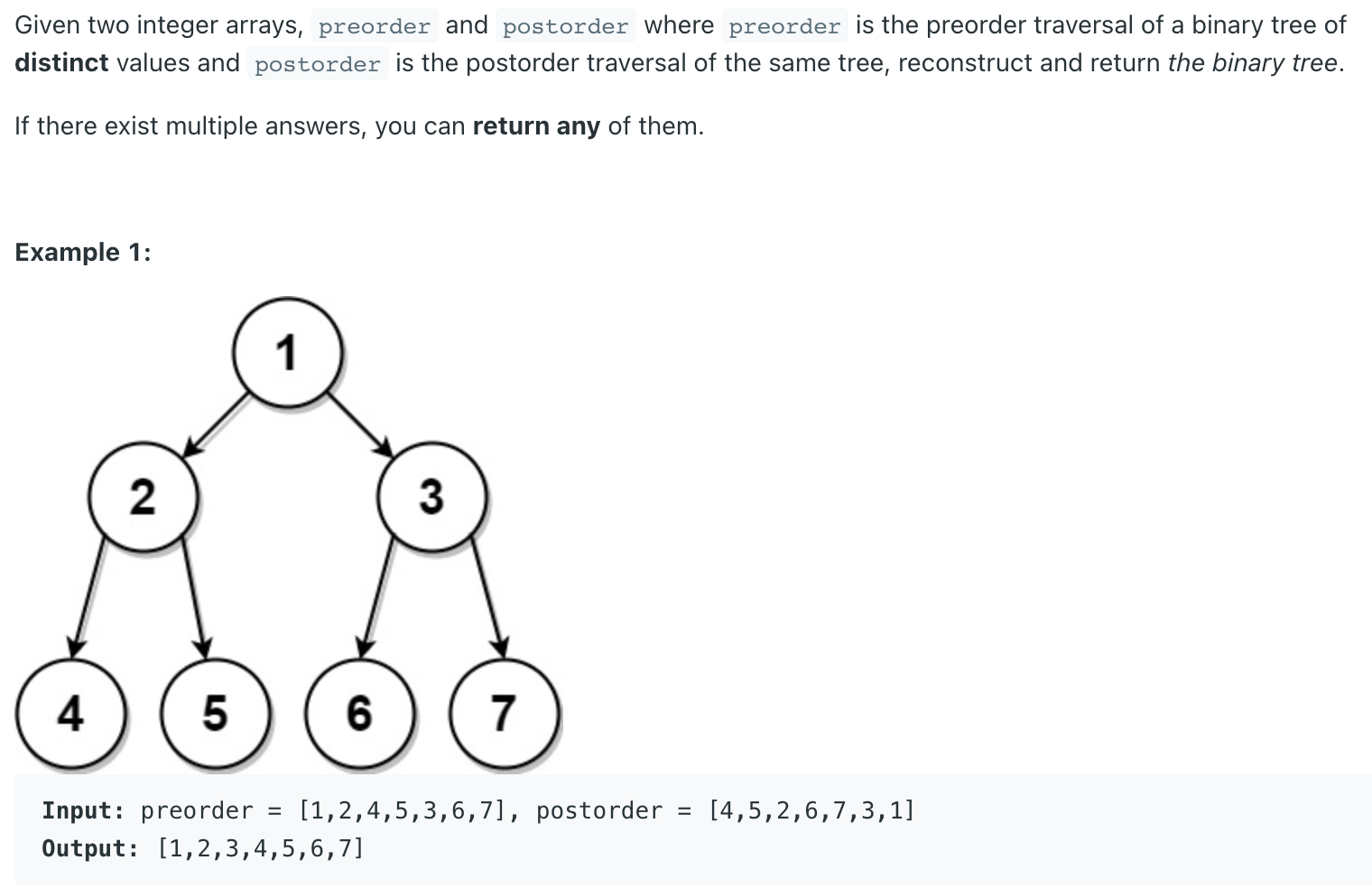
Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Postorder Traversal LeetCode Problem #889
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 class Solution {public TreeNode constructFromPrePost (int [] preorder, int [] postorder) {if (preorder.length == 0 || postorder.length == 0 ) {return null ;if (preorder.length == 1 ) {return (new TreeNode (preorder[0 ]));int rootVal = preorder[0 ];int leftSubNode = preorder[1 ];int rightSubNode = postorder[postorder.length-2 ];int i = 0 ;for (i=0 ;i<preorder.length;i++) {if (preorder[i] == rightSubNode) {break ;int j = 0 ;for (j=0 ;j<postorder.length;j++) {if (postorder[j] == leftSubNode) {break ;int [] preLeft;int [] preRight;if (preorder[i]==postorder[j]) {new int [0 ];else if (preorder.length==2 ) {1 ,2 );new int [0 ];else {1 ,i);int [] postLeft;int [] postRight;if (preorder[i]==postorder[j]) {0 ,j+1 );new int [0 ];else if (postorder.length==2 ) {0 ,1 );new int [0 ];else {0 ,j+1 );1 ,postorder.length-1 );TreeNode outTree = new TreeNode (rootVal);return outTree;
1.5 Level Order Traversal
Applied in Breadth-First Search, start with the root, first visit the root , then traverse its neighbors , second level neighbors ,…, so on and so forth.
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal LeetCode Problem #102
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();if (root == null ) {return outList;new LinkedList ();while (!queue.isEmpty()) {new ArrayList <>();int len = queue.size();for (int i=0 ;i<len;i++) {TreeNode inNode = queue.remove();if (inNode.left != null ) {if (inNode.right != null ) {return outList;
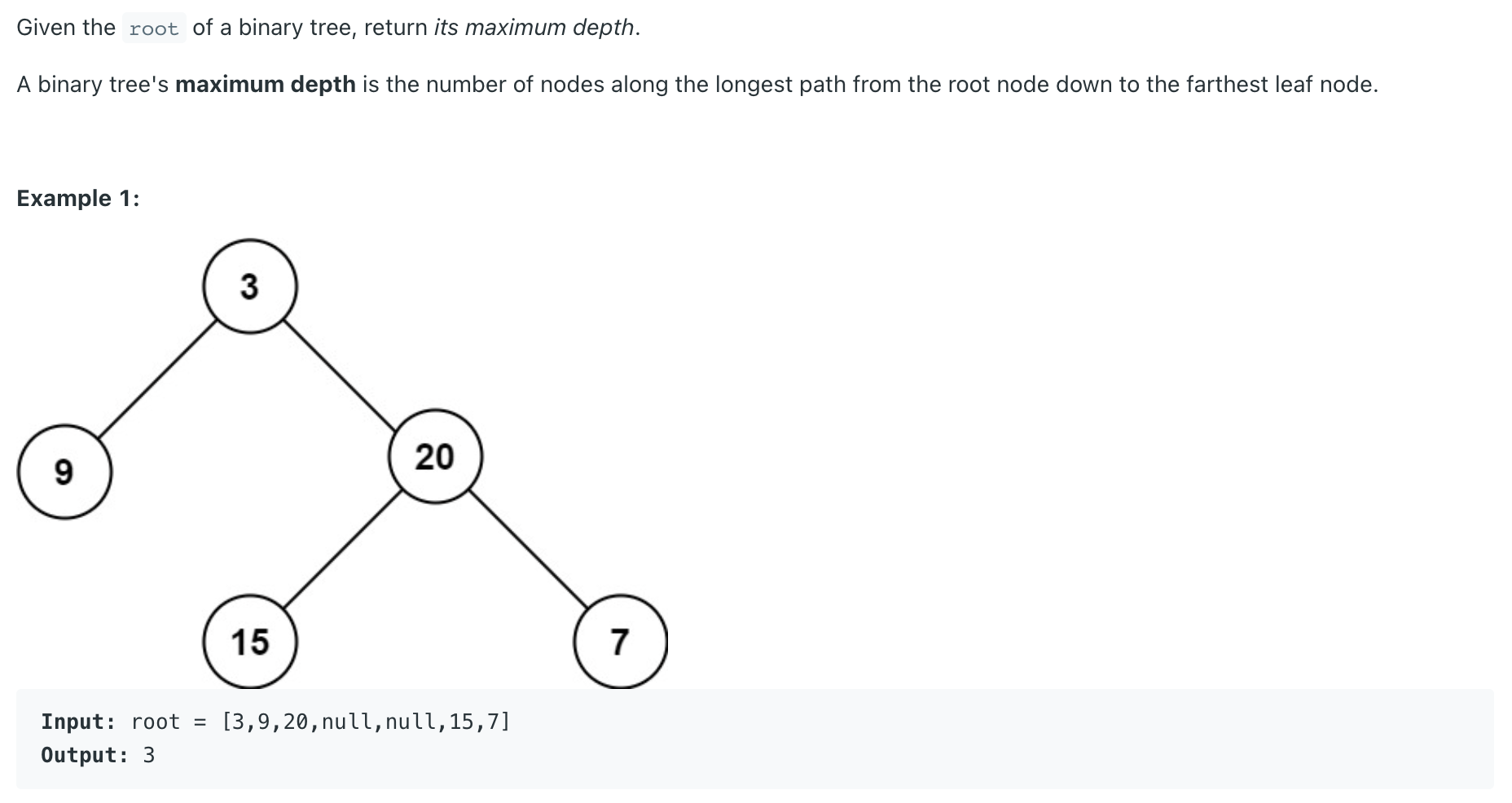
2 Classic Problem Maximum Depth of Binary Tree LeetCode Problem #104
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution {public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return 0 ;int left_depth = maxDepth(root.left);int right_depth = maxDepth(root.right);return Math.max(left_depth,right_depth)+1 ;
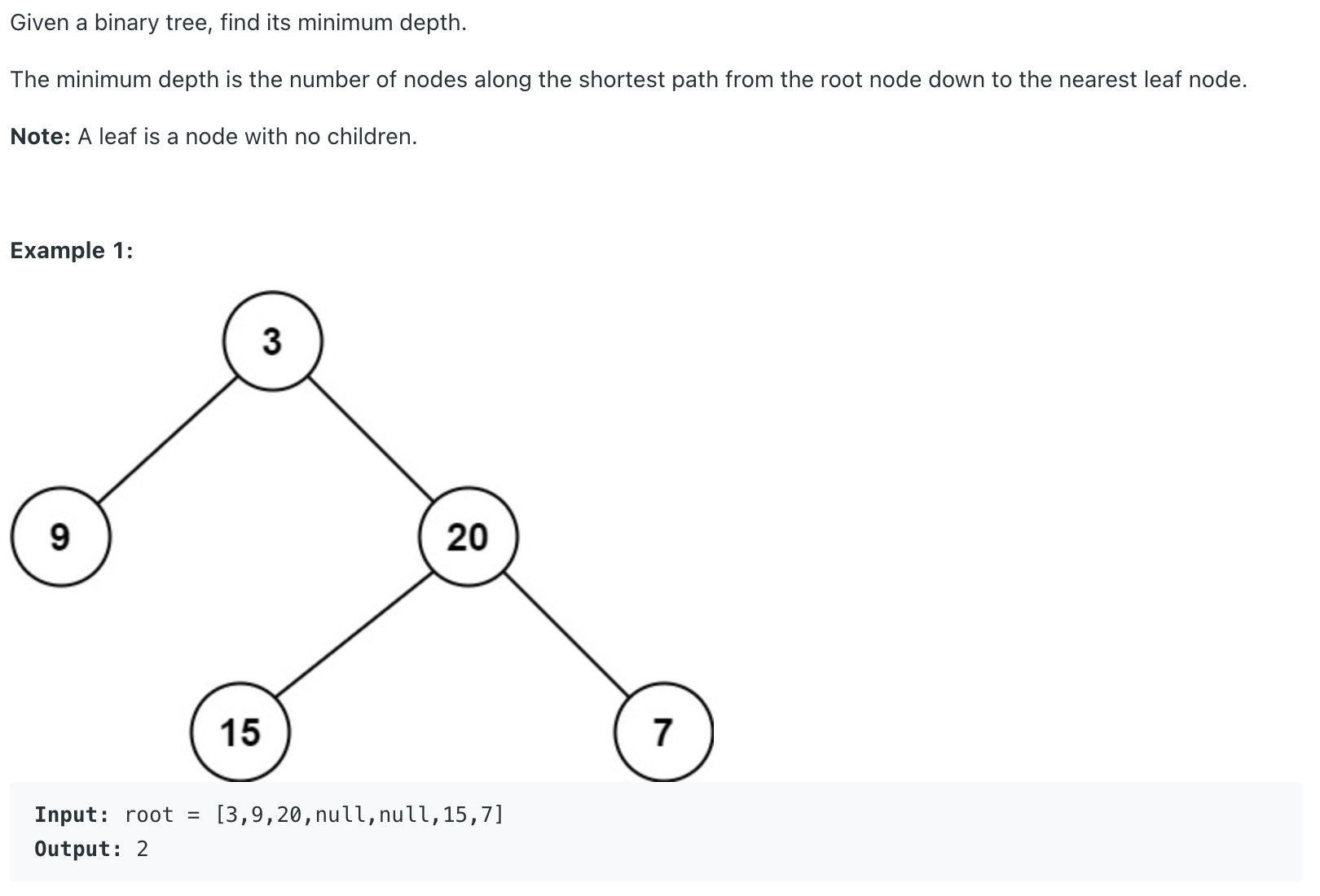
Minimum Depth of Binary Tree LeetCode Problem #111
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public int minDepth (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return 0 ;int left_depth = minDepth(root.left);int right_depth = minDepth(root.right);if (root.left==null ) {return right_depth+1 ;}if (root.right==null ) {return left_depth+1 ;}return Math.min(left_depth,right_depth)+1 ;
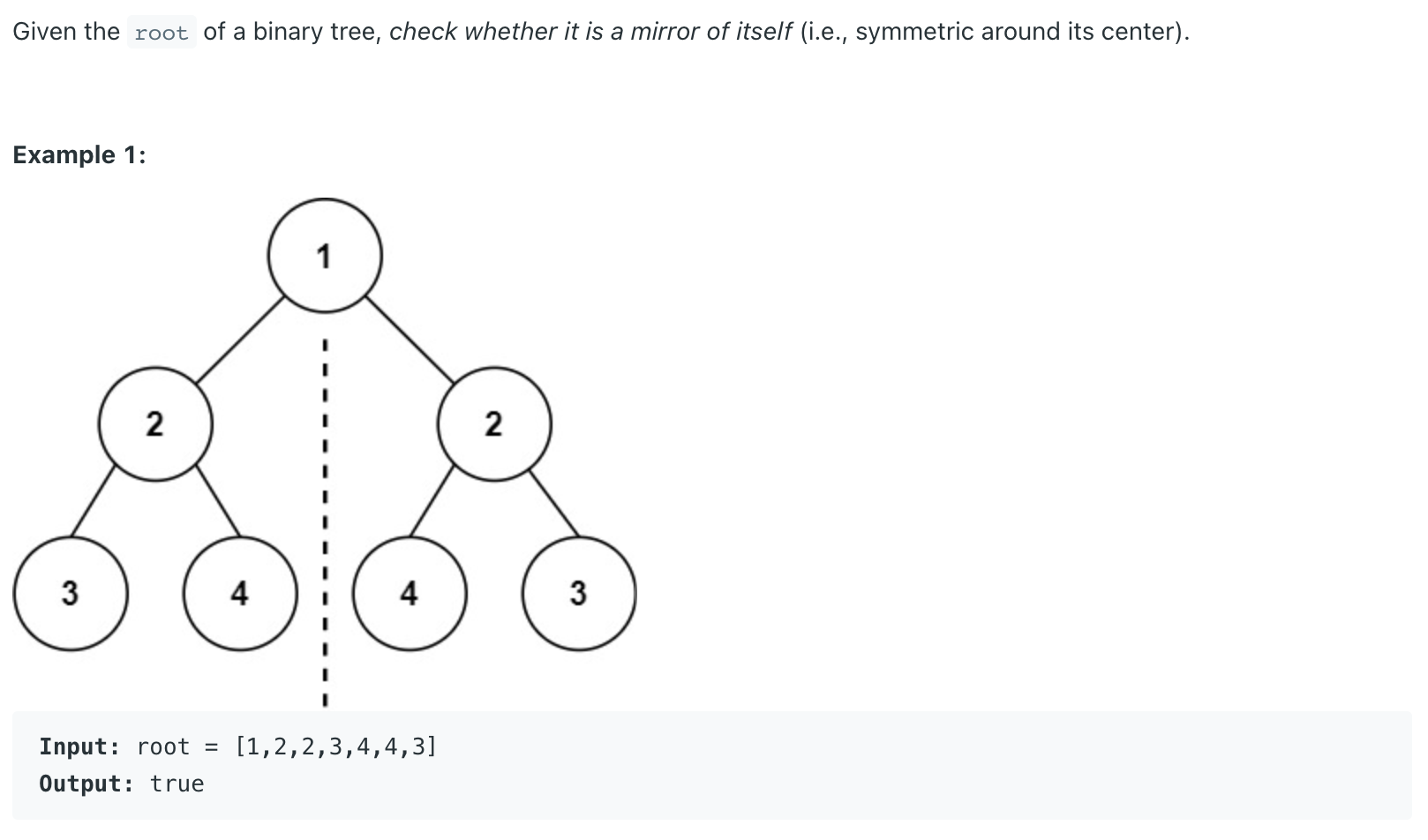
Symmetric Tree LeetCode Problem #101
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution {public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return true ;return check(root.left,root.right);boolean check (TreeNode l, TreeNode r) {if (l==null && r==null ) {return true ;}if (l==null || r==null ) {return false ;}if (l.val != r.val) {return false ;}return check(l.left,r.right) && check(l.right,r.left);
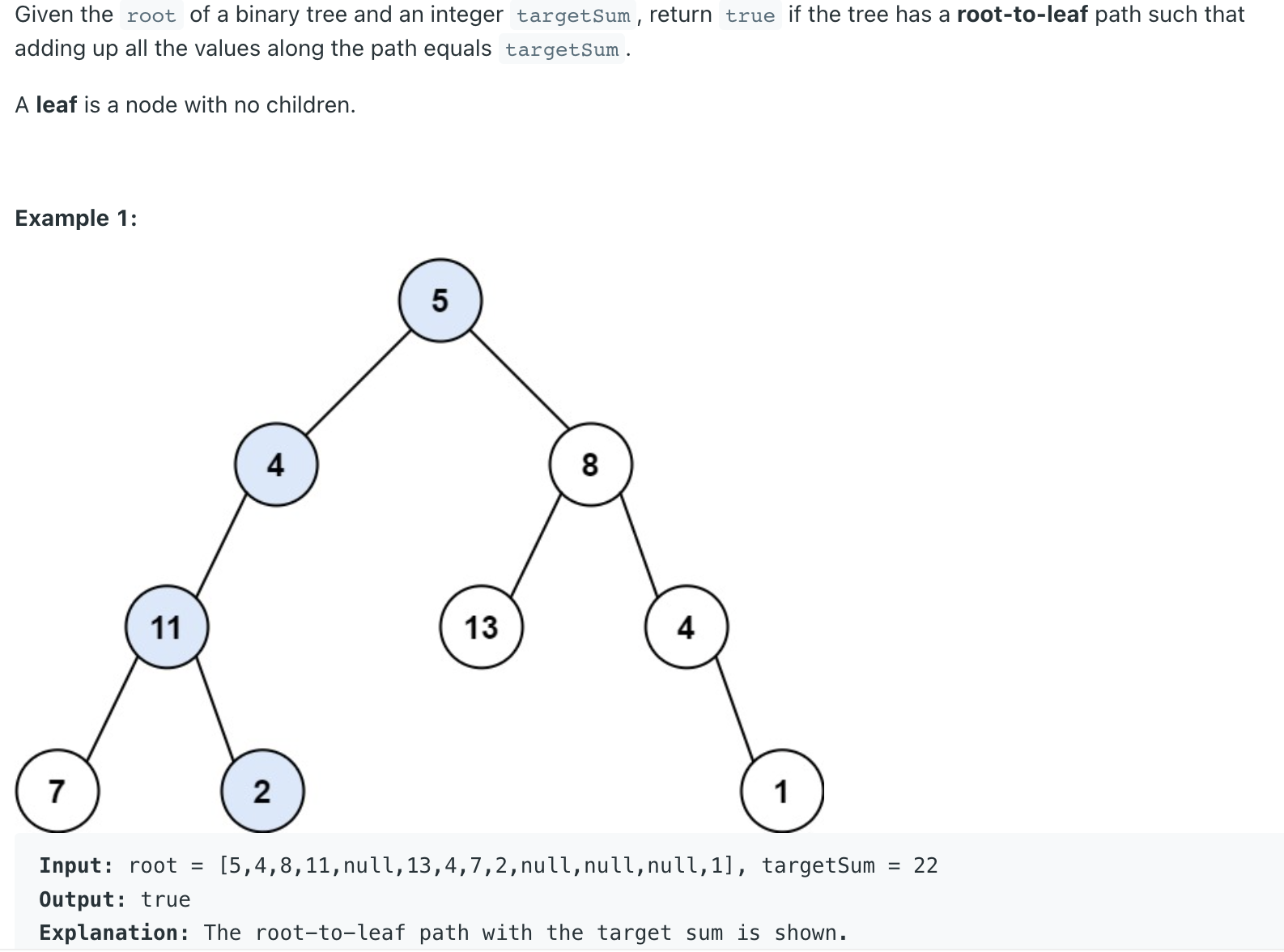
Path Sum LeetCode Problem #112
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution {public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null ) {return false ;}if (root.val == targetSum && root.left==null && root.right == null ) {return true ;return hasPathSum(root.left,targetSum-root.val)
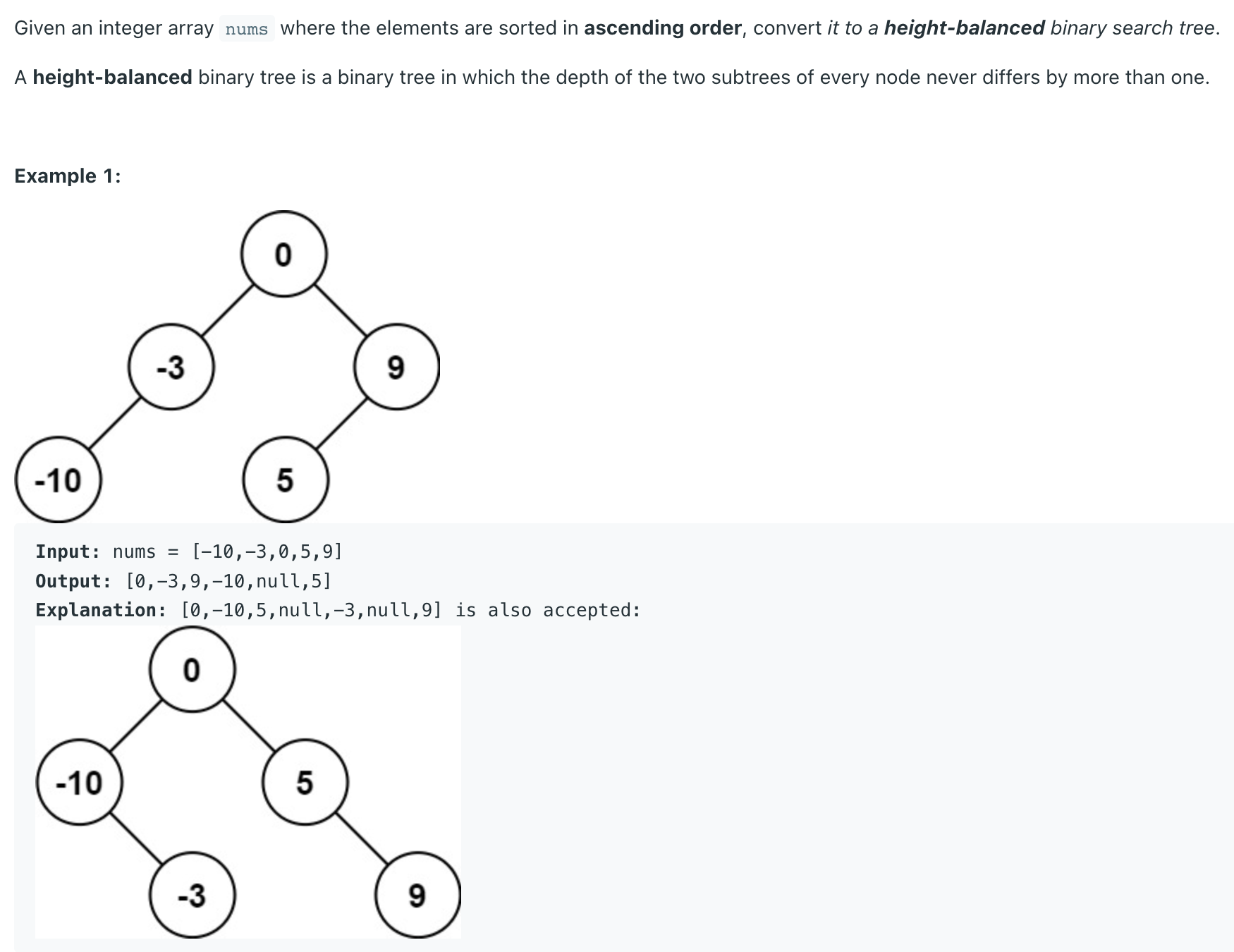
Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree LeetCode Problem #108
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST (int [] nums) {if (nums.length == 0 ) {return null ;}if (nums.length == 1 ) {return new TreeNode (nums[0 ]);}int mid = (nums.length-1 ) / 2 ;TreeNode outTree = new TreeNode (nums[mid]);int [] leftArr = Arrays.copyOfRange(nums,0 ,mid);int [] rightArr = Arrays.copyOfRange(nums,mid+1 ,nums.length);return outTree;
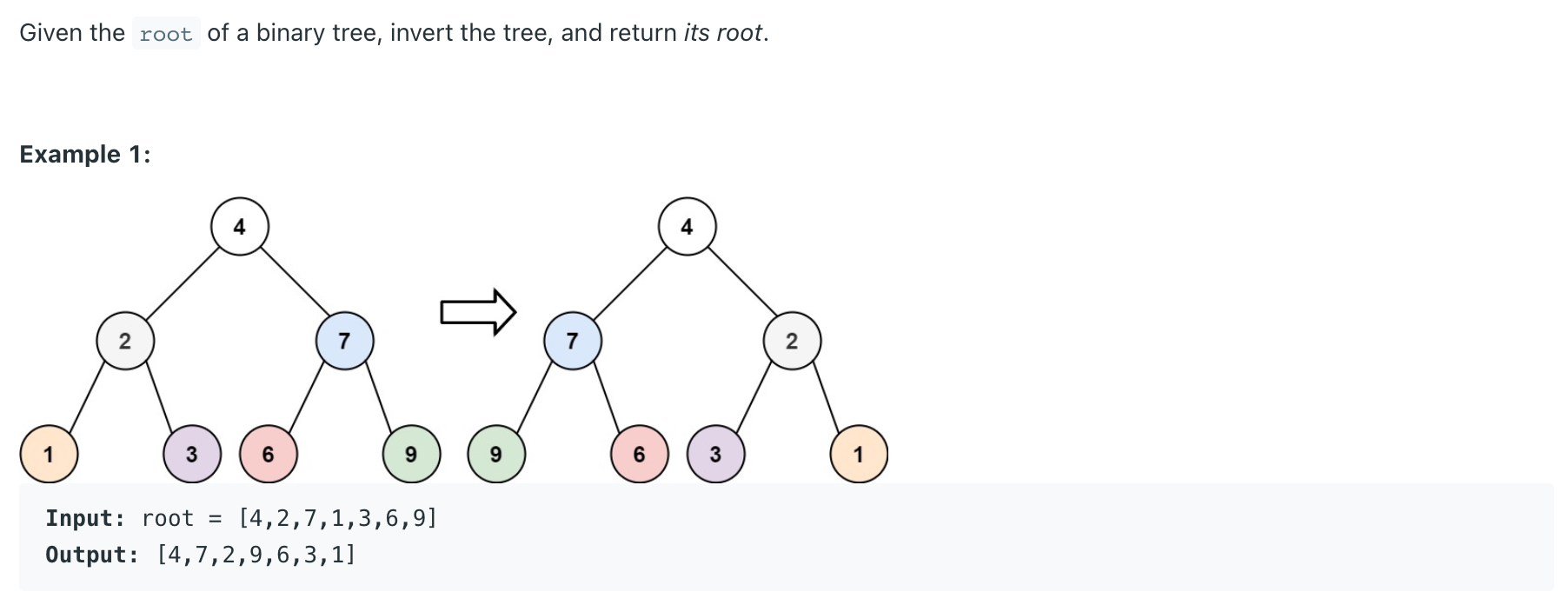
Invert Binary Tree LeetCode Problem #226
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return root;TreeNode temp = root.left;return root;
Last updated on 2022-11-25
References Binary Tree - Explore - LeetCode
写在最后 Binary Tree相关的知识会继续学习,继续更新.
原创文章,转载请标明出处 Made by Mike_Zhang
感谢你的支持